links:: Source Control for Test Automation with Git MOC
6. Git Branching Strategies
6. Git Branching Strategies
Git Flow
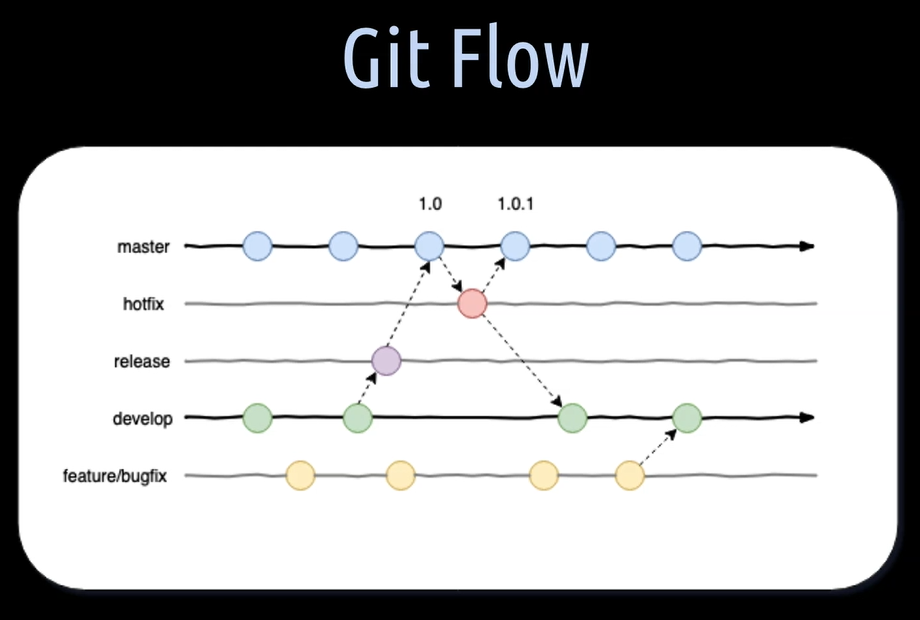
Git Flow is the most well-known branching strategy of them all. It was introduced by Vincent Driessen in 2010, and it's based on two branches.
One is called the Develop Branch.
It is the branch which contains the pre-production code. As soon a new feature is developed or a bug fix is done, it is merged into the develop branch. Often this branch then gets automatically deployed to a dev and/or to a test environment for testing.
When the source code in the develop branch reaches a stable point and is ready to be released, it is then merged into the main branch called master, where it is tagged with the release number.
The master branch should always reflect the production ready state.
During the development lifecycle, a variety of different supporting development branches are commonly used.
- Release branches for support preparations of a new production release
- Feature branches for the development of new features or tests
- Hot fix branches for immediate reactions upon critical issues, bugs in the master branch and additional bug fix branches for handling, let's say, normal bug fixes
Git Flow is useful when you have a well-defined numbered of releases per year.
It is also useful for large teams which build downloadable software packages and libraries where multiple versions of a project or product are in production.
Git Flow is less useful when you have small teams which need to iterate quickly, when you have to maintain a single version in production, and when you want to achieve continuous deployment and delivery.
GitHub Flow
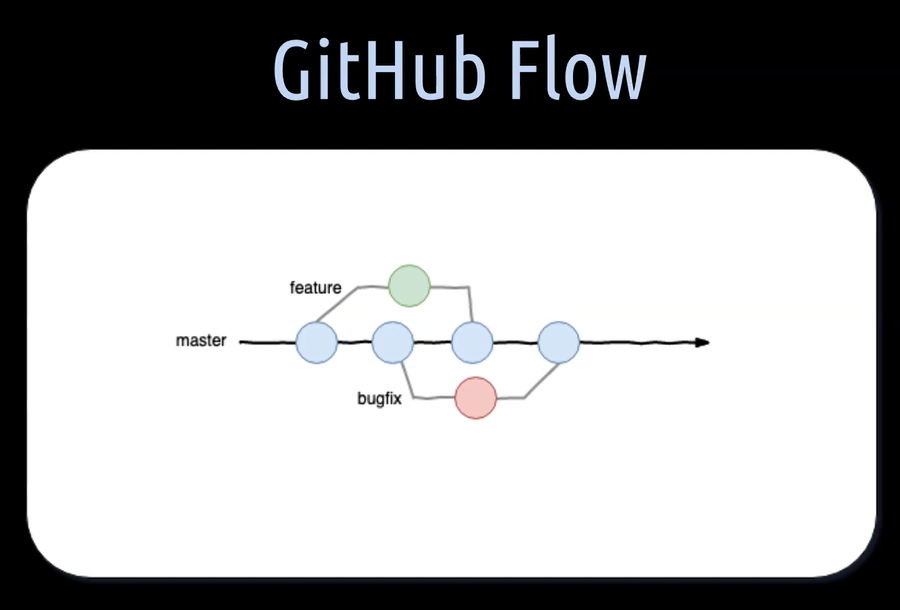
The GitHub Flow is a lightweight workflow created by GitHub itself in 2011.
It has some elements from the Git Flow, such as feature and bug fix branches, but there is only 1 main branch and that is the master branch.
It follows six simple principles.
- Anything in the master branch is deployable.
- Each time you create a new branch, for example, a feature or a bug fix branch, you branch away from the master branch.
- A local branch is regularly pushed through the same name branch on the remote repository to have a fast feedback from the CI server.
- When you need feedback or help, or you think the branch is ready for merging, open a pull request.
- After someone else has reviewed and signed off the feature, you can merge it into the master branch.
- Once it is merged into the master branch, you can and should deploy immediately to your test environment or directly to production, if that is possible in your context.
The GitHub Flow is useful when you want to achieve continuous deployment and delivery; when you want to work on an open source project; when you just have one single version of application code in production; or just one word version of a test automation framework to maintain.
The GitHub Flow is less useful when you need to maintain multiple versions of application code in production or test automation code.
Trunk-Based Development
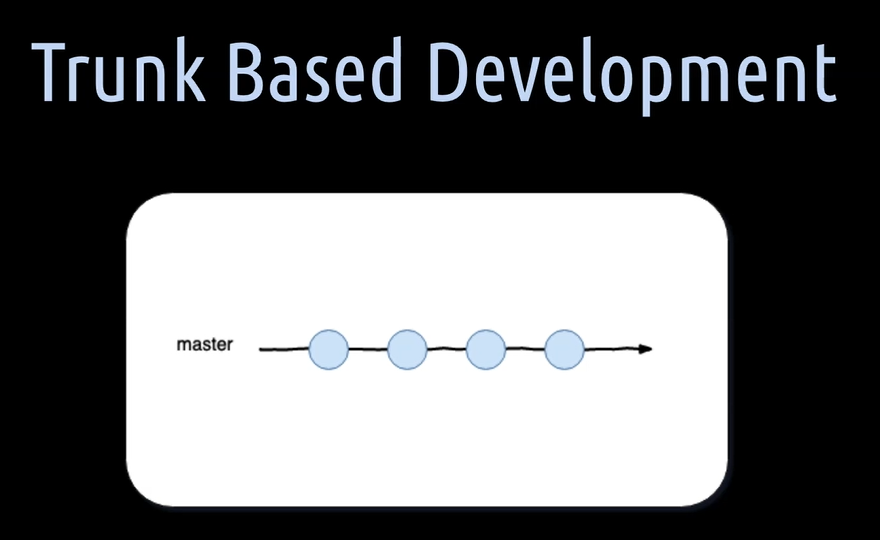
In Trunk Based development, short TBD, everyone is working on a single branch, usually the master branch with open access to it.
Open access means direct commits on master are not blocked, like it is often done in Git Flow or GitHub Flow. Everyone is committing directly to master without creating any pull request for demanding a review.
In some cases, it is also possible to create very short-lived feature or bug fix branches. Once the code on such a branch is compiled and all tests in the pipeline pass, it is merged straight away to master.
Trunk Based Development works best when you want to achieve continuous deployment and delivery.
It is also useful if you do pair programming or more programming as a whole team. Or if you're working in small teams with seasoned developers or automation engineers who need to iterate very quickly in their development life cycle.
Trunk based development can cause problems when you run an open source project, have lots of junior developers and/or automation engineers which are not doing pair or mob programming with some more experienced ones together, or you have to manage large teams.

My advice for your automation project is use or adapt the development of your test automation framework to one of these branching strategies, or even make up your very own branching strategy for your team and context.